Generative AI vs. Agentic AI: Understanding the Next Wave of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly evolving, and two prominent paradigms are shaping its future: generative AI and agentic AI. While both fall under the umbrella of AI, they possess distinct characteristics, capabilities, and implications. This blog post will delve into the key differences between these two approaches, shedding light on their potential impact across various industries.
Generative AI: The Creative Content Generator
Generative AI focuses on creating new content, such as text, images, audio, and video. It learns from existing data and generates outputs that resemble the training data. Popular examples include:
- Text generation: Tools like GPT-3 can write articles, poems, code, and even answer questions in a conversational manner.
- Image generation: Models like DALL-E 2 and Stable Diffusion can create realistic or artistic images from textual descriptions.
- Audio generation: AI can compose music, generate sound effects, and even synthesize speech.
- Video generation: AI can create short videos from text prompts or combine existing footage in novel ways.
Generative AI excels at tasks requiring creativity, content creation, and data augmentation. It has found applications in marketing, entertainment, education, and research.
Agentic AI: The Autonomous Decision-Maker
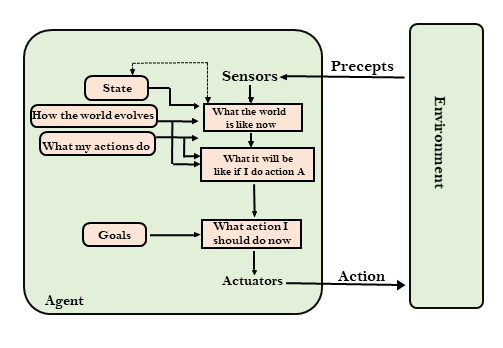
Agentic AI, on the other hand, emphasizes autonomous action and decision-making. An AI agent is designed to perceive its environment, reason about its goals, and take actions to achieve those goals. Key features of agentic AI include:
- Autonomy: Agents can operate independently without constant human supervision.
- Adaptability: Agents can learn from experience and adjust their behavior to changing environments.
- Goal-orientation: Agents are designed to achieve specific objectives.
- Interaction: Agents can interact with other agents and humans.
Agentic AI is well-suited for tasks requiring automation, problem-solving, and complex decision-making. Examples include:
- Robotics: Agents can control robots to perform tasks in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
- Game playing: AI agents can master complex games like chess and Go.
- Personal assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa can perform tasks on behalf of users.
- Financial trading: AI agents can automate trading decisions in financial markets.
Key Differences
| Feature | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
| Focus | Content creation | Autonomous action and decision-making |
| Output | New data (text, images, audio, video) | Actions in the environment |
| Goal | Generate realistic or creative content | Achieve specific objectives |
| Key Skills | Learning patterns, data generation | Reasoning, planning, problem-solving |
| Applications | Marketing, entertainment, education, research | Automation, robotics, decision support |
Implications
Generative AI and agentic AI have the potential to transform various industries. Generative AI can boost creativity, automate content creation, and personalize experiences. Agentic AI can improve efficiency, automate complex tasks, and enable new forms of human-machine collaboration.
As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge. However, it is important to consider the ethical implications of AI, such as bias, privacy, and job displacement. By addressing these challenges proactively, we can ensure that AI benefits society as a whole.
Key Takeaways
- Generative AI focuses on content creation, while agentic AI emphasizes autonomous action and decision-making.
- Generative AI excels at tasks requiring creativity and data augmentation, while agentic AI is well-suited for automation and problem-solving.
- Both generative AI and agentic AI have the potential to transform various industries, but it is important to consider the ethical implications of AI.
Sources: